Privacy Risks in Data Collection and Storage
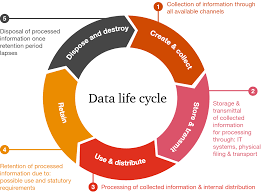
In today's digital world, personal data is collected and stored in unprecedented ways.
Companies collect immense amounts of user information through websites, apps, and online services, which may include sensitive data like browsing history, location, and financial details.
While this data enables personalized experiences and targeted advertising, it poses significant privacy risks.
If not stored properly or shared without the consent of the users, personal data can be misused by corporations or third parties.
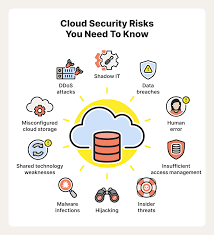
One of the major risks involves data breaches whereby cybercriminals access databases storing user information.
High-profile cases, such as the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal, have shown how data if mishandled, can compromise elections, manipulate opinions, and intrude on privacy.
Weak encryption and lax cybersecurity measures could also expose sensitive data to theft.
For example, Equifax, in 2017, had a breach that exposed the personal information of 147 million people because of an unpatched security flaw.
Organizations should implement robust encryption, update their security system from time to time, and adhere to data protection legislation such as GDPR.
On the users' part, it involves managing their privacy settings, adopting secure passwords, and selecting what information to put on the Internet.
Example: Equifax was in 2017 to expose Social Security numbers, birthdates, and addresses of millions of users,
a situation that proves the aftermath of poor data protection.
Misuse and Protection of Computing Resources
In this digital world, computing resources are part of every server, network, and personal device.
This can also be used as a means of misusing these very resources in terms of unauthorized access, denial of service due to overuse of resources, and other unlawful practices including mining malware and DDoS.
One of the most common misuses is botnets, networks of infected computers remotely controlled to conduct cyberattacks.
For example, the Mirai botnet used insecure IoT devices to run massive DDoS attacks that crippled major websites in 2016.
Inside an organization, employees may misuse resources by installing unauthorized software, which can create security vulnerabilities or performance issues.
These include cybersecurity policies, access controls, and network monitoring to protect computing resources.
Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits will help in preventing exploitation.
Users can also secure accounts by updating the software regularly, not downloading untrusted applications, and using multifactor authentication.
Example: The 2016 Mirai botnet attack used thousands of IoT devices to bring down popular services such as Twitter and Netflix.

Benefits and Risks of Computing Innovations
Computing innovations have transformed society and brought innumerable benefits to humans through communication, automation, and analyzing vast amounts of data.
Artificial Intelligence, Cloud computing, and blockchain disrupted major industries, enabling the healthcare, financial, and education sectors to go forward and prosper.
However, these innovations also introduce ethical and security concerns.
AI-powered facial recognition, for instance, enhances security but raises privacy issues and potential misuse in surveillance.
Additionally, automation and machine learning can lead to job displacement, with many industries shifting towards AI-driven processes.
A notable example is Amazon’s warehouse automation, which improves efficiency but reduces human labor needs.
Even with these risks, responsible innovation holds the greatest promise for ensuring maximum benefit and minimum harm.
Ethical guidelines, AI development with full transparency, and regulatory oversight will together ensure that computing advances serve society positively.
Understanding this balancing between technological progress and ethical responsibility is important for a sustainable digital future.
Example: While face recognition technologies have increased security, they have also given rise to serious surveillance issues and bias within the AI algorithm.

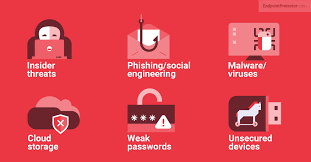
Unauthorized Access to Information
These teams do this through different methodologies: phishing, malware, social engineering, and exploitation of software vulnerability, whereby, through hacking or cybercrime, critical information is let out,
which more often than not leads to financial and reputational damages for individuals or organizations.
It is a technique adopted by attackers to make users reveal their login credentials through fake emails or websites.
For example, some cybercriminals utilized the COVID-19 pandemic and conducted phishing attacks in 2020 that stole personal information.
Keyloggers and ransomware compromise devices and extract confidential data.
The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack targeted hospitals and businesses around the world, locking critical files until ransom payments were made.
Organizations are available against unauthorized access with encryption, firewalls, and tight authentication.
In preventing unauthorized access, two-factor authentication, not clicking suspicious links, and the best antivirus software help.
Educating people on good cybersecurity practices helps to fight these risks.
Example: The WannaCry ransomware attack affected more than 200,000 computers worldwide, leveraging vulnerable Windows systems and demanding Bitcoin payments.

